[What is the internet?]
"internet" and "the Internet"
- internet (as a common noun)
- inter + network(s) <- any set of inter-connected networks
- regardless of the use of TCP/IP
- the Internet (as a proper noun)
- network of networks <- network of globally interconnected computer networks
- based on TCP/IP
Internet of X
- The Internet -> IoC(Internet of Computers)
- World Wide Web(WWW) -> IoD(Internet of Documents)
- Social Media / Web 2.0 -> IoP(Internet of People)
- Cloud Computing -> IoR(Internet of Resources)
- Things / Objects -> IoT(Internet of Things)
=> IoE(Internet of Everything)
X2X(Any to Any)
- X=Peer -> P2P(Peer-to-Peer) #전통적
- X=Machine -> M2M(Machine-to-Machine)
- X=Human -> H2X(Human-to-Any)
- X=Vehicle -> V2X(Vehicle-to-Vehicle)
- X=Online/Offline -> O2O(Online-to-Offline)
- X=AI -> AIoT(AI-to-Any, AI of Things or AI+X)
=> X2X(Any-to-Any)
[Internet Networking Architecture]
General Network Reference Model
- Core network
- mesh of interconnected routers
- network of networks
- two key core functions: forwarding, routing
- Access network
- connecting home/enterprise networks and end systems to core network
- use of various physical media
- Home/Enterprise network
- connecting end systems or hosts
- ecah host runs network applications
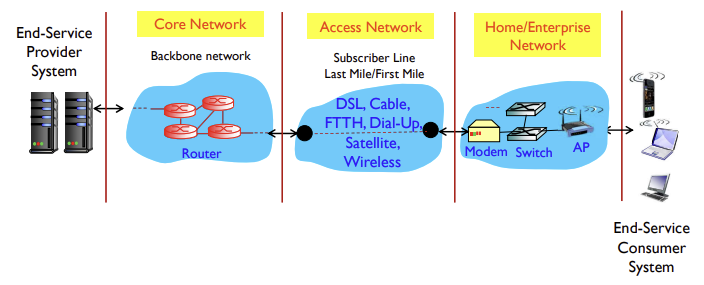
Internet Networking Architecture
1. 초기: full-mesh connection
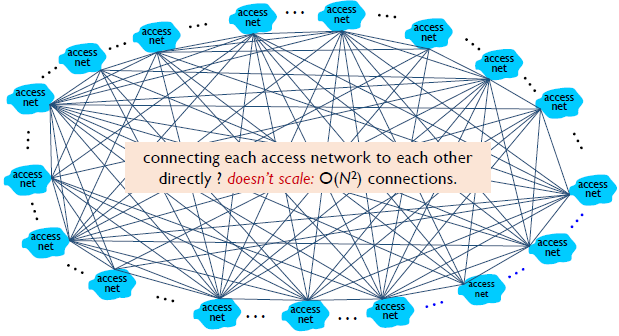
2. ISP(Internet Service Provider)
- an organization that provides services for accessing, using, the Internet

3. Network of Networks
- Networks are interconnected through multiple ISPs
- End systems connect to Internet via access ISPs
- Each regional ISP then connects to tier-1 ISPs
# IXP: operated by third party company to provide a meeting point to multiple ISPs

[Definition of Protocol]
Various definition on protocols
- Society
- etiquette
- politics: a formal agreement between nation states
- Science
- science: a predefined written procedural method of conducting experiments
- clinical trial: a document that plans a clinical trial
- Communications(통신)
- a defined set of rules and regulations that determine how data is transmitted
- in telecommunications and computer networking
Definition of Communication Protocol
- the set of conventions for the communicating entities to exchange information successfully
- What must confrom to successfully communicate for two entities?
- 주제: what is communicate
- 수단: how it is communicated
- 시간: when it is communicated
Key Elements of a Protocol
- Syntax #data format
- data formats
- encoding/defoding information
- signal level
- Semantics #actions taken on message transmission and receipt
- response
- control information
- error handling
- Timing #order of messages
- timeout
- sequence number
- speed matching
[Layered Protocol Models]
Benefits of a Layered Model
- changes in one layer do not affect other layers => independence
- assists in protocol design and implementation easy
- fosters competition among vendors at each layer
- better learning and understanding protocols
Requirements for successful communications
- Same number of layers at two entities
- Same protocol on each peer layer
- Same interface between upper & lower layers
Layered Protocol Reference Model
- Standardized Reference Protocol Architectures
- Any device can communicate with others
- Any vendors can provide marketable products
- Customers can choose communication devices independent of vendors
- OSI(Open Systems interconnection) Reference Model
- Official standard by ISO
- Seven layers
- delivered too late
- TCP/IP protocol suite
- The de facto standard
- Five layers
- Most widely used
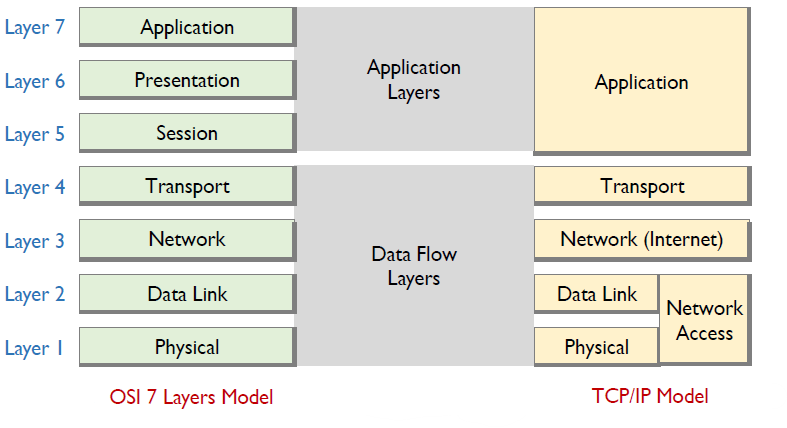
OSI 7 Layers Model
- Application layer: means for application to access OSI environment
- Presentation layer
- define data formats to applications
- Example services
- Data formats
- coding
- Data compression
- Encryption
- Session layer : control od fialogues between applications
- Transport layer
- logical communcation to exchange data
- between application layer processes
- running on different hosts(end systems)
- common transport layer services
- error free, in sequence
- no losses, no duplications
- quality of service
- logical communcation to exchange data
- Network layer
- logical communication to transport packets
- between identified (addressed) end systems
- not needed on direct links
- Basic network layer services
- routing
- forwarding
- logical communication to transport packets
- Data Link layer
- Reliable delicery of frames between terminals
- over a physically connected common local media
- Datalink layer services
- framing
- MAC(Media Access Control)
- error detection and control
- flow contro
- Reliable delicery of frames between terminals
- Physical layer : physical interface between devices
TCP/IP Model
- Five layers
- Application
- supporting network applications
- FTP, SMTP, HTTP, e-mail, P2P
- Transport
- data transfer between app.processes
- TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)
- UDP(User Datagram Protocol)
- Network
- routing of datagrams from source to destination
- IP(Internet Protocol)
- optionally, ICMP, IGMP, ARP
- Link: frame delivery between neighboring network elelments
- Physical: bits "on the wire"
- Application
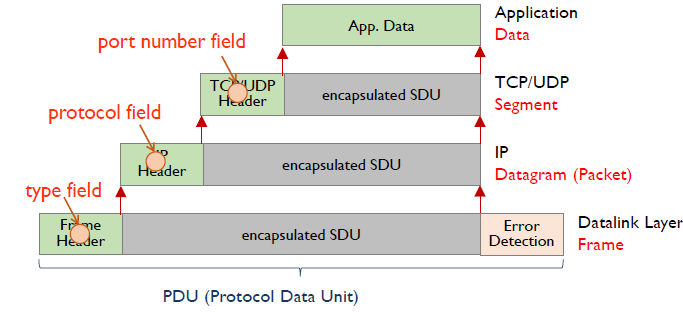
- Encapsulation
- interfacing towards lower layers
- each layer takes SDU(Service Data Unit) from its upper layer -> appends header -> delivers PDU(header+SDU, Protocol Data Unit) to its lower layer
- does not modify any bit of the message(SDU)
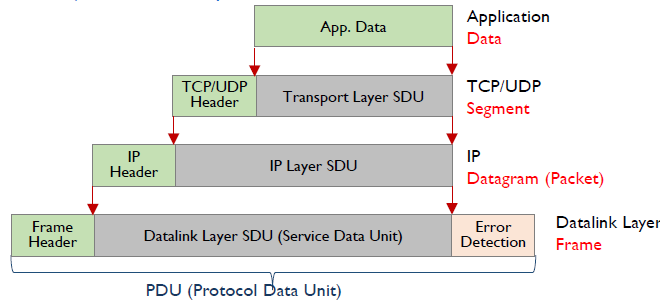
- Decapsulation
- interfacing towards upper layers
- each layer has a specific field in its header to indicate the upper layer protocol for the SDU to be delivered.
[Why All-IP?]
IP(Internet Protocol)
- the only one protocol at network layer of TCP/IP model
# many protocols exist at other layers.
Role of IP Layer
- Internetworking heterogeneous networks <- integration tool
- Solution for the integration of network applications
- a Unified viewpoint of the Internet users
'CS > 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [TCP/IP] Transport Layer - UDP (0) | 2024.11.11 |
|---|---|
| [TCP/IP] Transport Layer - Overview (0) | 2024.11.11 |
| [TCP/IP] Application Layer - P2P Model (0) | 2024.11.11 |
| [TCP/IP] Application Layer - CS Model (0) | 2024.11.11 |
| [TCP/IP] Application Layer - Overview (0) | 2024.11.11 |



